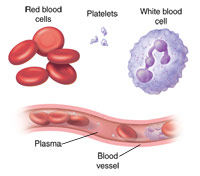
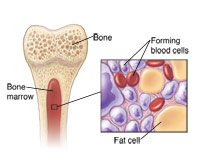
What Are White Blood Cells?
Your blood is made up of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma.
Your white blood cells account for only about 1% of your blood, but their impact is big. White blood cells are also called leukocytes. They protect you against illness and disease.
Think of white blood cells as your immunity cells. In a sense, they are always at war. They flow through your bloodstream to fight viruses, bacteria, and other foreign invaders that threaten your health. When your body is in distress and a particular area is under attack, white blood cells rush in to help destroy the harmful substance and prevent illness.
White blood cells are made in the bone marrow. They are stored in your blood and lymph tissues. Because some white blood cells called neutrophils have a short life less than a day, your bone marrow is always making them.
Types of white blood cells
Among your white blood cells are:
-
Monocytes. They have a longer lifespan than many white blood cells and help to break down bacteria.
-
Lymphocytes. They create antibodies to fight against bacteria, viruses, and other potentially harmful invaders.
-
Neutrophils. They kill and digest bacteria and fungi. They are the most numerous type of white blood cell and your first line of defense when infection strikes.
-
Basophils. These small cells seem to sound an alarm when infectious agents invade your blood. They secrete chemicals, such as histamine, a marker of allergic disease, that help control the body's immune response.
-
Eosinophils. They attack and kill parasites and cancer cells, and help with allergic responses.
Problems affecting white blood cells
Your white blood cell count can be low for a number of reasons. This includes when something is destroying the cells more quickly than the body can replenish them. Or when the bone marrow stops making enough white blood cells to keep you healthy. When your white blood cell count is low, you are at great risk for any illness or infection, which can spiral into a serious health threat.
Your healthcare provider can do a blood test to see whether your white blood cell count is normal. If your count is too low or too high, you may have a white blood cell disorder.
A number of diseases and conditions may affect white blood cell levels:
-
Weak immune system. This is often caused by illnesses, such as HIV/AIDS, or by cancer treatment. Cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy can destroy white blood cells and leave you at risk for infection.
-
Infection. A higher-than-normal white blood cell count usually means you have some type of infection. White blood cells are multiplying to destroy the bacteria or virus.
-
Myelodysplastic syndrome. This condition causes abnormal production of blood cells. This includes white blood cells in the bone marrow.
-
Cancer of the blood. Cancers including leukemia and lymphoma can cause uncontrolled growth of an abnormal type of blood cell in the bone marrow. This results in a greatly increased risk for infection or serious bleeding.
-
Myeloproliferative disorder. This disorder refers to various conditions that trigger the excessive production of immature blood cells. This can result in an unhealthy balance of all types of blood cells in the bone marrow and too many or too few white blood cells in the blood.
-
Medicines. Some medicines can raise or lower the body's white blood cell count.
Conditions, such as extreme physical stress caused by an injury or emotional stress, can also trigger high white blood cell levels. So can inflammation, labor or the end of pregnancy, smoking, or even extreme exercise.
Medical Reviewers:
- Jessica Gotwals RN BSN MPH
- Ronald Karlin MD
- Todd Gersten MD