What is multiple sclerosis?
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a long-lasting (chronic) disease of the central nervous system. It is thought to be an autoimmune disorder, a condition in which the body attacks itself by mistake. MS is an unpredictable disease that affects people differently. Some people with MS may have only mild symptoms. Others may lose their ability to see clearly, write, speak, or walk when communication between the brain and other parts of the body becomes disrupted.
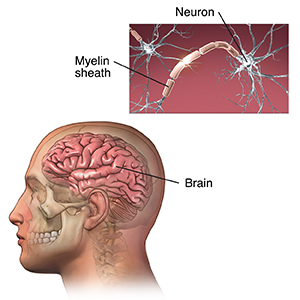
Myelin is a protein and fatty substance that surrounds and protects nerve fibers. In MS, the immune system attacks the myelin, which becomes destroyed in many areas. This loss of myelin forms scar tissue called sclerosis. These areas are also called plaques or lesions. When the nerves are damaged in this way, they can’t conduct electrical impulses normally to and from the brain.
When MS causes repeated attacks, it's called relapsing remitting MS. When the symptoms progress over time without clear attacks, it's called primary progressive MS.
What causes multiple sclerosis?
There are many possible causes of MS, such as:
Autoimmune disorders
Infectious agents, such as viruses
Environmental factors
Genetic factors
What are the symptoms of multiple sclerosis?
The symptoms of MS are often unpredictable. They may be mild or severe, short-term or long-lasting. They may appear in different combinations, depending on the area of the nervous system affected. The following are the most common symptoms of MS. But each person may have different symptoms.
First symptoms of MS
Blurred or double vision
Red-green color distortion
Pain and loss of vision because of swelling of the optic nerve (optic neuritis)
Trouble walking and difficulty with balance
An abnormal feeling, such as numbness, prickling, or pins and needles (paresthesia)
Other symptoms of multiple sclerosis
Muscle weakness in the arms and legs
Trouble with coordination. You may have problems walking or standing. You may also be partly or completely paralyzed.
Spasticity. This is the involuntary increased tone of muscles leading to stiffness and spasms.
Fatigue. This may be brought on by physical activity. But it may ease with rest. You may have constant tiredness that doesn't go away.
Loss of feeling
Speech problems
Tremor
Dizziness
Hearing loss
Bowel and bladder problems
Depression
Changes in sexual function
About half of all people with MS have thinking (cognitive) problems linked to the disease. The effects of these problems may be mild. Your healthcare provider may only find them after much testing. The problems may be with:
Focusing (concentration)
Attention
Memory
Poor judgment
Symptoms of MS are grouped as primary, secondary, or tertiary as described below:
Primary symptoms. These symptoms are a direct result of the destruction of myelin:
| Secondary symptoms. These are complications that may occur as a result of the primary symptoms, for example:
| Tertiary symptoms. These are social, job-related, and psychological problems:
|
The symptoms of MS may look like other health problems. Always talk with your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How is multiple sclerosis diagnosed?
Not one specific test is used to diagnose MS. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and signs, imaging tests, and lab tests. A healthcare provider can make a diagnosis by following a careful process to rule out other causes and diseases. Two things must be true to make a diagnosis of relapsing remitting MS:
You must have had 2 attacks at least 1 month apart. An attack is when any MS symptoms show up suddenly. Or when any MS symptoms get worse for at least 24 hours.
You must have more than 1 area of damage to the central nervous system myelin. Myelin is the sheath that surrounds and protects nerve fibers. This damage must have occurred at more than 1 point in time and not have been caused by any other disease.
Your healthcare provider will ask about your health history and do a neurological exam. This includes:
Mental functions
Emotional functions
Language functions
Movement and coordination
Vision
Balance
Functions of the 5 senses
You may also need:
MRI. This diagnostic test uses a combination of large magnets and a computer to make detailed pictures of organs and structures within the body without the use of X-rays. It can find plaques or scarring caused by MS. Generally, a single attack along with certain patterns of changes in brain tissue seen on an MRI scan of the brain done with contrast can mean that you have MS.
Evoked potentials. These tests record the brain's electrical response to visual, auditory, and sensory stimuli. These tests show if you have a slowing of messages in the different parts of the brain.
Cerebrospinal fluid analysis. This is also called a spinal tap or lumbar puncture. It looks at the fluid taken from the spinal column to make an evaluation or diagnosis. This test checks for cellular and chemical abnormalities seen with MS.
Blood tests. These are done to rule out other causes for various neurological symptoms.
Eye exam and visual fields measurements.
How is multiple sclerosis treated?
Treatment will depend on your symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how bad the condition is.
Currently, treatments are divided into:
Disease-modifying treatments. These directly target inflammation in the central nervous system. They help slow its deterioration.
Treatment of acute relapses. The use of steroids and plasma exchange (PLEX) can speed up your recovery when you have an MS attack.
There is no known cure for MS. But you can do things to help change the course of the disease, treat flare-ups, manage symptoms, and improve your function and mobility.
Treatments for the conditions seen with MS may include:
Medicines (talk with your provider to see what medicines may be an option for you)
Equipment, such as canes, braces, or walkers
Rehabilitation activities
Rehab varies depending on your symptoms and how bad they are. MS rehab may help you to:
Get back functions that are important for daily living
Be as independent as you can
Involve your family
Make the right decisions relating to your care
Learn about equipment like canes, braces, or walkers that can make is easier to move around
Set up an exercise program that builds muscle strength, endurance, and control
Get back motor skills
Speak more easily if you have weakness or a lack of coordination of face and tongue muscles
Manage bowel or bladder incontinence
Relearn thinking skills
Change the way your home is set up to keep you safe but allow you to move about as easily as possible
What are possible complications of multiple sclerosis?
The complications of MS range from mild to severe. They can range from fatigue to the inability to walk. Other problems include loss of vision, balance, and bowel or bladder control. Depression can result from the difficulty of living with a chronic condition.
Living with multiple sclerosis
It's important to take your medicines as directed. You may get help by taking part in a clinical trial. Using equipment like canes or walkers can help you get around as walking becomes harder to do. Rehab activities can also help you keep or get back functioning. Changing the way your home is set up can help you stay independent. Talk with your family and healthcare providers about what you need.
Key points about multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease of the central nervous system.
MS is unpredictable. Some people may be only mildly affected. Others may lose the ability to see clearly, write, speak, or walk.
Early symptoms can include vision problems, trouble walking, and tingling feelings.
MS affects people differently. But common problems are trouble with movement and thinking, and bowel and bladder incontinence.
Medicines and rehabilitation can help to keep or restore functioning.
Next steps
Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your healthcare provider:
Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen.
Before your visit, write down questions you want answered.
Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your provider tells you.
At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Also write down any new instructions your provider gives you.
Know why a new medicine or treatment is prescribed, and how it will help you. Also know what the side effects are and when they should be reported.
Ask if your condition can be treated in other ways.
Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
Know what to expect if you do not take the medicine or have the test or procedure.
If you have a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for that visit.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
What is multiple sclerosis?
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a long-lasting (chronic) disease of the central nervous system. It is thought to be an autoimmune disorder, a condition in which the body attacks itself by mistake. MS is an unpredictable disease that affects people differently. Some people with MS may have only mild symptoms. Others may lose their ability to see clearly, write, speak, or walk when communication between the brain and other parts of the body becomes disrupted.
Myelin is a protein and fatty substance that surrounds and protects nerve fibers. In MS, the immune system attacks the myelin, which becomes destroyed in many areas. This loss of myelin forms scar tissue called sclerosis. These areas are also called plaques or lesions. When the nerves are damaged in this way, they can’t conduct electrical impulses normally to and from the brain.
When MS causes repeated attacks, it's called relapsing remitting MS. When the symptoms progress over time without clear attacks, it's called primary progressive MS.
What causes multiple sclerosis?
There are many possible causes of MS, such as:
-
Autoimmune disorders
-
Infectious agents, such as viruses
-
Environmental factors
-
Genetic factors
What are the symptoms of multiple sclerosis?
The symptoms of MS are often unpredictable. They may be mild or severe, short-term or long-lasting. They may appear in different combinations, depending on the area of the nervous system affected. The following are the most common symptoms of MS. But each person may have different symptoms.
First symptoms of MS
-
Blurred or double vision
-
Red-green color distortion
-
Pain and loss of vision because of swelling of the optic nerve (optic neuritis)
-
Trouble walking and difficulty with balance
-
An abnormal feeling, such as numbness, prickling, or pins and needles (paresthesia)
Other symptoms of multiple sclerosis
-
Muscle weakness in the arms and legs
-
Trouble with coordination. You may have problems walking or standing. You may also be partly or completely paralyzed.
-
Spasticity. This is the involuntary increased tone of muscles leading to stiffness and spasms.
-
Fatigue. This may be brought on by physical activity. But it may ease with rest. You may have constant tiredness that doesn't go away.
-
Loss of feeling
-
Speech problems
-
Tremor
-
Dizziness
-
Hearing loss
-
Bowel and bladder problems
-
Depression
-
Changes in sexual function
About half of all people with MS have thinking (cognitive) problems linked to the disease. The effects of these problems may be mild. Your healthcare provider may only find them after much testing. The problems may be with:
-
Focusing (concentration)
-
Attention
-
Memory
-
Poor judgment
Symptoms of MS are grouped as primary, secondary, or tertiary as described below:
|
Primary symptoms. These symptoms are a direct result of the destruction of myelin:
|
Secondary symptoms. These are complications that may occur as a result of the primary symptoms, for example:
|
Tertiary symptoms. These are social, job-related, and psychological problems:
|
The symptoms of MS may look like other health problems. Always talk with your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How is multiple sclerosis diagnosed?
Not one specific test is used to diagnose MS. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and signs, imaging tests, and lab tests. A healthcare provider can make a diagnosis by following a careful process to rule out other causes and diseases. Two things must be true to make a diagnosis of relapsing remitting MS:
-
You must have had 2 attacks at least 1 month apart. An attack is when any MS symptoms show up suddenly. Or when any MS symptoms get worse for at least 24 hours.
-
You must have more than 1 area of damage to the central nervous system myelin. Myelin is the sheath that surrounds and protects nerve fibers. This damage must have occurred at more than 1 point in time and not have been caused by any other disease.
Your healthcare provider will ask about your health history and do a neurological exam. This includes:
-
Mental functions
-
Emotional functions
-
Language functions
-
Movement and coordination
-
Vision
-
Balance
-
Functions of the 5 senses
You may also need:
-
MRI. This diagnostic test uses a combination of large magnets and a computer to make detailed pictures of organs and structures within the body without the use of X-rays. It can find plaques or scarring caused by MS. Generally, a single attack along with certain patterns of changes in brain tissue seen on an MRI scan of the brain done with contrast can mean that you have MS.
-
Evoked potentials. These tests record the brain's electrical response to visual, auditory, and sensory stimuli. These tests show if you have a slowing of messages in the different parts of the brain.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid analysis. This is also called a spinal tap or lumbar puncture. It looks at the fluid taken from the spinal column to make an evaluation or diagnosis. This test checks for cellular and chemical abnormalities seen with MS.
-
Blood tests. These are done to rule out other causes for various neurological symptoms.
-
Eye exam and visual fields measurements.
How is multiple sclerosis treated?
Treatment will depend on your symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how bad the condition is.
Currently, treatments are divided into:
-
Disease-modifying treatments. These directly target inflammation in the central nervous system. They help slow its deterioration.
-
Treatment of acute relapses. The use of steroids and plasma exchange (PLEX) can speed up your recovery when you have an MS attack.
There is no known cure for MS. But you can do things to help change the course of the disease, treat flare-ups, manage symptoms, and improve your function and mobility.
Treatments for the conditions seen with MS may include:
-
Medicines (talk with your provider to see what medicines may be an option for you)
-
Equipment, such as canes, braces, or walkers
-
Rehabilitation activities
Rehab varies depending on your symptoms and how bad they are. MS rehab may help you to:
-
Get back functions that are important for daily living
-
Be as independent as you can
-
Involve your family
-
Make the right decisions relating to your care
-
Learn about equipment like canes, braces, or walkers that can make is easier to move around
-
Set up an exercise program that builds muscle strength, endurance, and control
-
Get back motor skills
-
Speak more easily if you have weakness or a lack of coordination of face and tongue muscles
-
Manage bowel or bladder incontinence
-
Relearn thinking skills
-
Change the way your home is set up to keep you safe but allow you to move about as easily as possible
What are possible complications of multiple sclerosis?
The complications of MS range from mild to severe. They can range from fatigue to the inability to walk. Other problems include loss of vision, balance, and bowel or bladder control. Depression can result from the difficulty of living with a chronic condition.
Living with multiple sclerosis
It's important to take your medicines as directed. You may get help by taking part in a clinical trial. Using equipment like canes or walkers can help you get around as walking becomes harder to do. Rehab activities can also help you keep or get back functioning. Changing the way your home is set up can help you stay independent. Talk with your family and healthcare providers about what you need.
Key points about multiple sclerosis
-
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease of the central nervous system.
-
MS is unpredictable. Some people may be only mildly affected. Others may lose the ability to see clearly, write, speak, or walk.
-
Early symptoms can include vision problems, trouble walking, and tingling feelings.
-
MS affects people differently. But common problems are trouble with movement and thinking, and bowel and bladder incontinence.
-
Medicines and rehabilitation can help to keep or restore functioning.
Next steps
Tips to help you get the most from a visit to your healthcare provider:
-
Know the reason for your visit and what you want to happen.
-
Before your visit, write down questions you want answered.
-
Bring someone with you to help you ask questions and remember what your provider tells you.
-
At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis, and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Also write down any new instructions your provider gives you.
-
Know why a new medicine or treatment is prescribed, and how it will help you. Also know what the side effects are and when they should be reported.
-
Ask if your condition can be treated in other ways.
-
Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
-
Know what to expect if you do not take the medicine or have the test or procedure.
-
If you have a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for that visit.
Medical Reviewers:
- Anne Fetterman RN BSN
- Heather M Trevino BSN RNC