Areas of Expertise
Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rsfMRI)
rsfMRI is a powerful tool to examine the spontaneous neural activity in the brain during rest. Measuring the low-frequency fluctuations (LFFs: 0.01 Hz – 0.1 Hz) in the blood-oxygen level dependent (BOLD) signal, we can investigate the functional communications between spatially distinct brain regions.
References:
- Arefin TM, Mechling AE, Meirsman AC, Bienert T, Hübner NS, Lee HL, et al. Remodeling of Sensorimotor Brain Connectivity in Gpr88 -Deficient Mice. Brain Connect. 2017 Oct;7(8):526–40.
- Mechling, AE, Arefin TM, Lee HL, Bienert T, Reisert M, Ben Hamida S, et al., Deletion of the mu opioid receptor gene in mice reshapes the reward-aversion connectome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2016. 113(41): p. 11603-11608.
Awake Functional MRI
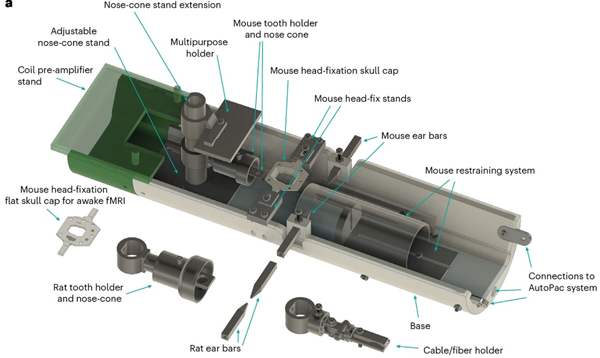
Imaging rodents in awake state offers a means to eliminate the confounding effects of anesthesia and the challenges involving interspecies translation (rodents to human). This approach further allows us to examine the relationship between brain and behavior in conscious animals.
References:
- Arefin TM*, Ben Youss Z*, Qayyum S. Yi R, Zhnag J, Wadghiri YZ, et al. Open-source versatile 3D-print animal conditioning platform design for in vivo preclinical brain imaging in awake mice and anesthetized mice and rats. Lab Anim 53, 33–42 (2024). (*Co-1st author)
Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging (dMRI)
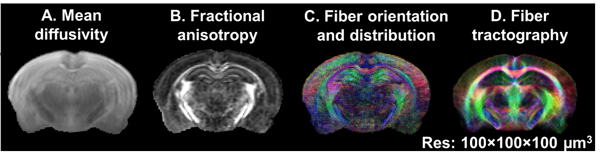
dMRI is one of the most widely used non-invasive techniques that traces diffusion of water molecules along the axons to map the structural networks in the brain. dMRI provides multi-level information about the brain microstructural fingerprints including morphology, and brain network properties. Additionally, with the advent of high-resolution dMRI acquisition and tractography methods, dMRI tractography permits simultaneous examination of multiple white matter connections in the entire brain without tissue sectioning reducing the time and cost of the experiments.
References:
- Arefin TM, Lee CH, White JD, Zhang J, Kaffman A. Macroscopic Structural and Connectome Mapping of the Mouse Brain Using Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Bio Protoc. 2021 Nov 20;11(22):e4221
- Arefin TM, Lee CH, Liang Z, Rallapalli H, Wadghiri YZ, Turnbull DH, et al. Towards reliable reconstruction of the mouse brain corticothalamic connectivity using diffusion MRI. Neuroimage. 2023 Jun;273:120111.
Manganese-Enhancement MRI (MEMRI)
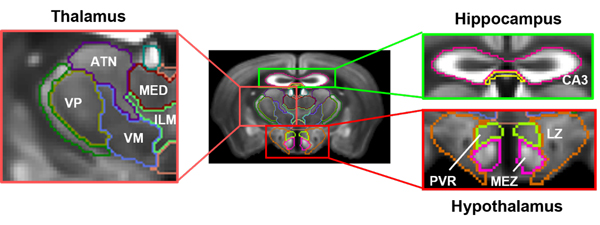
MEMRI is a non-invasive technique that can be used to investigate neurobiological systems with enhanced MR contrast and relatively high spatial resolution using the paramagnetic divalent ion manganese (Mn2+). The chemical similarities between the Mn2+ and calcium (Ca2+) allow Mn2+ to enter excitable cells via voltage-gated calcium channels, the sodium (Na+)/ Ca2+ exchanger, and the Na+/magnesium (Mg2+) antiporter. Therefore, MEMRI technique has the potential to reveal morphological information of the brain as well as to map neuronal tracts by exploring Mn2+ transportation across synapses in the living brain.
References:
- Arefin TM, Lee CH, Liang Z, Rallapalli H, Wadghiri YZ, Turnbull DH, et al. Towards reliable reconstruction of the mouse brain corticothalamic connectivity using diffusion MRI. Neuroimage. 2023 Jun;273:120111.
Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Perfusion MRI
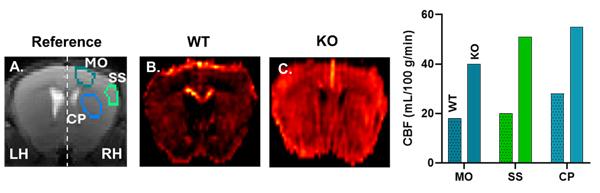
ASL Perfusion MRI is a non-invasive tool to assess the spatial distribution of microvascular blood flow. ASL does not require exogenous contrast agent, rather uses endogenous intravascular tracer-hydrogen nuclei in the blood to map the cerebral blood flow (CBF) in murine models of human pathology.
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS)
MRS is a non-invasive technique to measure the chemical composition of tissues in the brain and other organs. Quantification of the MR-observable metabolites can provide considerable biochemical information to the investigators to better understand the role of metabolites in normal and pathological conditions.
Assessment of mouse behavior using IntelliCage
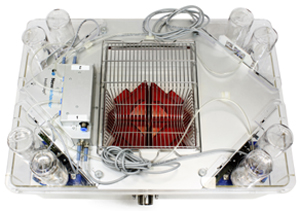 IntelliCage is a home-cage-based rodent behavioral assessment platform that can be used to investigate the neurobehavioral underpinnings in rodent models of human disporders. This fully automated live-in environment system helps eliminating the confounding effects and considerable stress from environmental and experimental variables that may obscure the behavioral measures.
IntelliCage is a home-cage-based rodent behavioral assessment platform that can be used to investigate the neurobehavioral underpinnings in rodent models of human disporders. This fully automated live-in environment system helps eliminating the confounding effects and considerable stress from environmental and experimental variables that may obscure the behavioral measures.